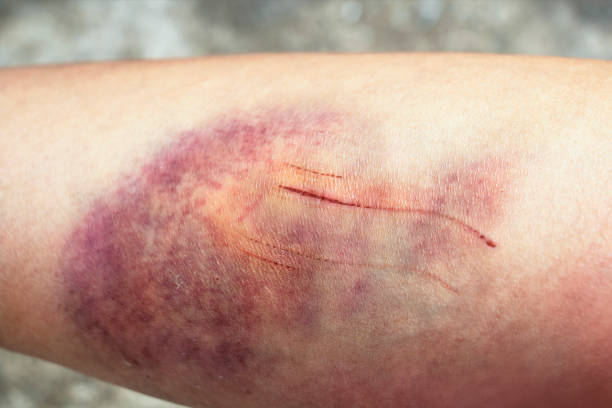
What is a scab?
After your skin is damaged, a scab forms.
A blood clot forms when you rub your knee skin. This eventually turns into a protective layer. The scab will be removed, and your tissue will regenerate.
Although it may not be obvious, a scab can often indicate healthy healing. Depending on the severity of your wound, recovery may take several days or even weeks.
What is the cause of scabs?
As a defense against infection and blood loss, scrubs form.
A scrape will cause platelets, also known as blood clot cells, to begin to clot to stop bleeding and prevent fluid from escaping. The scab is formed when the blood or wound dries.
Scabs are not only common cuts or scrapes but can also be caused by:
- dry, cracking skin
- acne
- Bug bites
- fungal infection
- Bacterial infection
- eczema
- psoriasis
- herpes
- Chickenpox
Treatment of scabs
Although scabs can heal themselves, the healing process can take longer if the wound is more serious. These are some tips to speed up scab healing.
Make sure you keep your scab clean.
Keeping your scab clean and all other injuries at bay is essential. You can increase your chances of infection by removing debris and germs. This will slow down your healing.
Use mild soap and warm water to wash the scab gently. Avoid scratching your scab by not scrubbing. It can cause your skin to bleed, heal, and possibly scare.
Make sure to keep your wounds moist.
The American Academy of Dermatology states that keeping your wounds moisturized speeds up your skin’s healing and recovery. Dry wounds can quickly form a scab, slowing down your healing process. You can prevent your injuries from getting worse by moistening them.
To keep your wounds or scabs moist, dermatologists recommend using petroleum jelly daily.
Do not pick your scab!
It can be tempting to pick at your scabs, especially if they start itching. These actions can lead to new trauma and slow down your recovery. You can also increase your chances of getting an infection by picking at your scabs, which can cause swelling and pain.
Both hot and cold therapy
Warm compresses stimulate blood flow to the wound and promote skin regeneration. Warm compresses can treat scabs and prevent them from drying out.
A cold compress can be applied to the affected area, similar to a warm one. It can reduce swelling and provide itching relief. Cold therapy can also help reduce inflammation. Talk to your doctor about using an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drug as part of your wound treatment.
Preventive measures are essential.
Cover your scab with a bandage if you are active or if it is still very fresh. This will prevent irritation and reduce the chance of it being scraped. Excessive trauma to the scab can cause bleeding and swelling and slow down your healing.
Outlook
Although they are an essential part of healing, they can make your wounds more visible if you have large areas. They can be treated at home to speed up your recovery.
Your doctor should be consulted if you notice signs of infection or if the scabs don’t shrink.